Acupuncture and Neurotransmitters
Acupuncture and Neurotransmitters
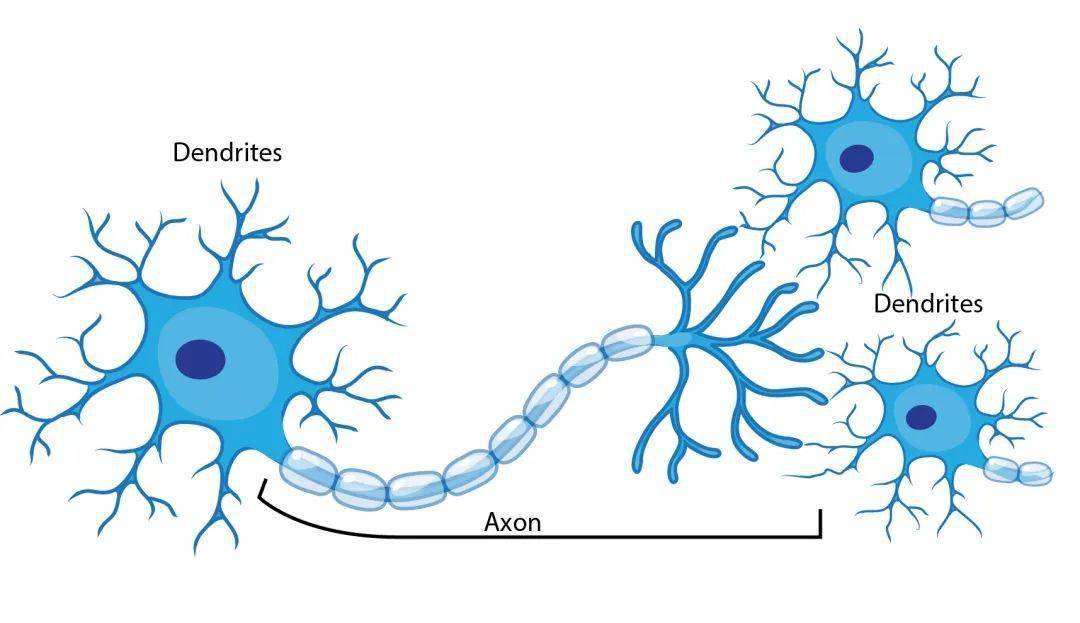
Acupuncture signals, whether generated by manual acupuncture or electroacupuncture, significantly affect the release, synthesis, reuptake and degradation of central neurotransmitters/regulators, including monoamines (such as serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine), acetylcholine (ACh), amino acids, pain sensitins, substance P, prostaglandins, cholecystokinin octapeptide-8 (CCK-8), somatostatin and neurotrophic factors.

In general, acupuncture enhances the activity of endogenous opioid peptides, serotonin, dopamine, ACh, and inhibitory amino acids such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABa), glycine, taurine, and lactams, while attenuating the activity of norepinephrine and excitatory amino acids including glutamate and aspartate. Acupuncture for a long time may result in an overproduction of CCK-8 and the depletion of some pre-acupuncture substances, resulting in acupuncture tolerance.
acupuncture also regulates the expression and function of the corresponding receptors. However, the effect of acupuncture on central neurotransmitters/modulators depends on the state of the organism and the condition of acupuncture, and differs from region to region in the central nervous system.
neurotransmitters play a crucial role in neural communication, affecting everything from involuntary movement to learning to emotion. The system is complex and highly interconnected. Neurotransmitters function in specific ways, but they can also be affected by external physical factors, diseases, drugs, and even other chemical messengers.